The Magic in Botanical Derived Terpenes: A Guide to BDT in Cannabis

What determines a plant’s flavor and smell? Terpenes of course! They are the rich hydrocarbon compounds that determine the unique smell and flavor found in all plants including cannabis, and even some animals. BDT refers to botanical terpenes that are derived from plant sources such as citrus fruits, black pepper, lemongrass, lavender, and several other herbs.
BDT can be added to cannabis products to vamp up the flavor, smell, and better yet, the effects. But, don’t let this confuse you with CDT, which are the terpenes derived from cannabis (Cannabis Derived Terpenes). This article is going to explain the role of BDT and CDT, their differences, similarities, and their qualities that make weed just oh so good.

Some well-known examples of BDT are:
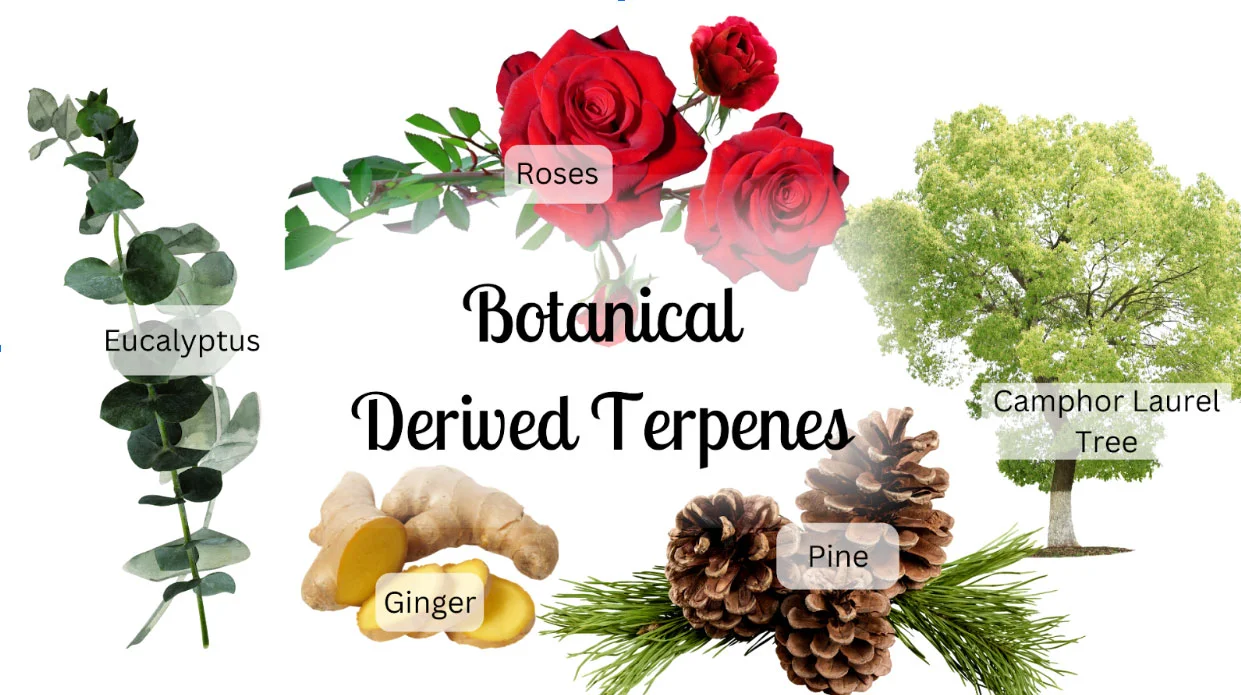
Geraniol – extracted from roses
Limonene – found in citrus fruits like limes, lemons, and oranges
Camphor – present in the camphor laurel tree
Cymene – derived from tangerines
Borneol – found in rosemary and ginger
Terpinene – extracted from eucalyptus
It’s worth noting that there is a third category of terpenes known as synthetic terpenes. Unlike CDT and BDT, synthetic terpenes are not naturally extracted but are produced in laboratories. Consequently, they may have a different chemical composition compared to naturally derived terpenes (CDT and BDT). Plus, both CDT and BDT, as well as synthetically made terpenes, can be used in the production of vape cartridges and other cannabinoid products.
Terpenes can be extracted from their natural sources and utilized in various products such as food, drinks, and even cannabis vapes. Mother nature herself has over 200 different types of terpenes, each with its own distinct aroma, taste, and potential effects on the body.

Although further research is required to fully comprehend their effects, some studies indicate that certain terpenes may offer health benefits. Common botanical terpenes, like citrus, mint, pine, and lavender, are popular examples. By extracting terpenes from common plants, a natural and potent flavor experience can be created as a more cost-effective option compared to those derived from cannabis.
Generally, they are extracted through a method called “steam distillation“. This is the same method used to extract flavors for drinks like hard seltzers and fruit-infused sparkling water. The whole process involves putting the plant material in boiling water to create steam that carries the essential oils, including terpenes, from the plant. The steam is then condensed down and cooled in order to collect the essential oils, which can be infused into cannabis oils and concentrates used in weed vapes.

Just like how essential oils are traditionally used in aromatherapy to evoke certain feelings or moods, such as relaxation with lavender or mental clarity with citrus, terpenes also have specific effects that we are all drawn to.
Because they are derived from real plants and not artificially created in a lab, botanical terpenes have a more genuine flavor that many people prefer. Their fruity and flavorful aroma makes BDT vapes discreet and suitable for use almost anywhere, making them a convenient option for those new to cannabis or exploring vaporization.
When creating concentrates for vapes and other products, cannabis brands can carefully select botanical terpenes to replicate the aroma, flavor, and even the therapeutic effects of a specific cannabis strain. This allows them to craft an authentic, flavor-focused experience that is similar yet more accessible, and always naturally derived.
The term BDT in delta 8 refers to products that include terpenes derived from both botanical sources and cannabis. Similarly, CDT in delta 8 indicates that the delta 8 distillate has been enhanced with terpenes derived from cannabis.

The key to maintaining consistent botanical terpenes ultimately boils down to one concept: isolation. When a terpene is properly isolated and obtained from a plant that is cultivated in very similar conditions to other batches of the same isolate, the brand can ensure a higher level of consistency.
The increasing popularity of indoor hydroponic growing has significantly improved the consistency of terpene isolates. You can compare your terpenes to the experience of tasting wine at a small vineyard.
The chemical composition of a CDT and BDT is identical. This means that a terpene extracted from a cannabis plant is the same as a terpene extracted from another plant in terms of structure and chemical properties. For example, pinene extracted from pine plants and cannabis plants will have the same chemical makeup and structure.
A significant difference in comparison is the availability of terpenes. Botanically derived terpenes are more easily accessible for bulk purchase compared to terpenes derived from cannabis. This is due to the greater availability of botanical materials and the lower yield of terpenes obtained from a cannabis plant. With higher availability, it’s likely that prices will be lower.